Cybercriminals steal credit card? Cybercriminals have various methods at their disposal to hack and exploit credit card...

Cybercriminals steal credit card? Cybercriminals have various methods at their disposal to hack and exploit credit card...
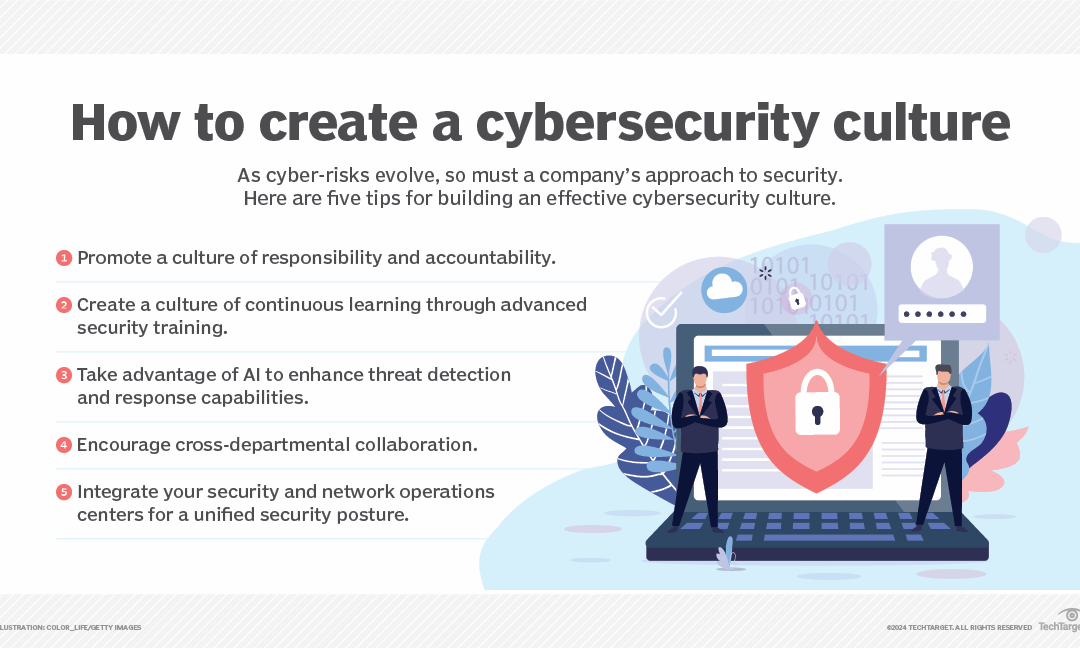
This in-depth cybersecurity planning guide provides information and advice to help organizations develop a successful strategy...

While home health agencies face distinct health IT challenges, collaboration and innovation are crucial for overcoming these...

The umbrella term malware is one of the greatest cybersecurity threats enterprises face. Learn about 12 common types of malware...

Originally Published on TechTarget.com by Sharon Shea, Executive Editor and Alexander S. Gillis, Technical Writer and Editor...
In today’s interconnected world, phishing attacks remain one of the most dangerous and prevalent cybersecurity threats. They manifest through various channels such as emails, phone calls, text messages, and even fake websites. Phishing attempts aim to deceive individuals and organizations into disclosing sensitive information. As a result, businesses must recognize the growing risk of phishing and take proactive steps to protect their assets, reputation, and data.
Phishing is a type of cyber attack where malicious actors impersonate trustworthy entities to deceive victims into revealing sensitive information, such as login credentials, credit card numbers, or confidential business data. These attacks can happen via different methods, including email, phone calls, text messages, and fake websites. The main goal of phishing is to exploit human behavior and weaknesses to bypass security systems, making it one of the most effective and damaging forms of cybercrime.
Human Error: Despite advanced cybersecurity technologies, humans remain the weakest link in the security chain. Phishing attacks rely heavily on social engineering, using tactics that exploit emotions like fear, greed, and urgency. For example, a victim may receive an email stating, “Your account has been compromised—click here to reset your password,” or “You’ve won a prize, claim it now!” These scams aim to make individuals act without thinking, often leading to unintentional breaches of security.
Phishing Statistics: Phishing continues to grow as a threat, with significant increases in attacks across all communication channels. Consider the following statistics:
Email Phishing: Approximately 1.2% of all emails sent globally are malicious, amounting to about 3.4 billion phishing emails daily. In 2022, 84% of organizations experienced at least one phishing attempt, marking a 15% increase from the previous year.
Phone Call Phishing (Vishing): The FBI has identified phishing as the third most common scam, with phone-based phishing attempts (vishing) becoming increasingly prevalent. In sectors like hospitality, AI-driven voice phishing has surged, where attackers mimic the voices of executives to trick employees into transferring funds or sharing confidential data.
Text Message Phishing (Smishing): Mobile phishing has grown exponentially, increasing by 475% from 2019 to 2020. Fraudulent text messages now account for 19.2 billion monthly messages in the U.S., highlighting the scale of smishing attempts.
Fake Websites: Phishing isn’t limited to emails. Fraudsters use fake websites and social media platforms to deceive users into revealing their personal information. The rise of AI technologies has made these scams more sophisticated, with attackers creating highly convincing fake websites and communications that are more difficult to spot.
Financial Loss and Data Breaches: Phishing attacks can result in substantial financial losses, data breaches, and intellectual property theft.
One example is the 2015 phishing attack on Ubiquiti Networks, which led to the theft of $46.7 million. The company’s financial employees received emails from attackers impersonating company executives, asking for large fund transfers. Ubiquiti was unable to recover the stolen funds, and the breach raised questions about the company’s internal controls and email security protocols.
Another high-profile case occurred in 2020, when Verizon Business fell victim to a phishing campaign targeting corporate clients. The attackers impersonated company executives to gain access to sensitive internal communications and data. While Verizon quickly contained the breach, this incident highlighted how phishing can infiltrate even large organizations and compromise valuable business assets.
Reputation Damage: Phishing attacks can severely damage a company’s reputation, especially if the breach leads to the exposure of customer data. If clients, customers, or partners lose trust in your ability to safeguard sensitive information, the long-term impact can be devastating. Rebuilding trust after a major phishing attack can be a time-consuming and costly process, and it can have lasting effects on your bottom line.
Phishing as a Gateway to Other Cyber Threats: Phishing often serves as a precursor to other, more damaging cyber attacks. Once attackers gain access to a company’s network through phishing, they may install malware or ransomware, or use compromised credentials to launch further attacks. These threats can cause significant business disruptions, intellectual property theft, and long-term operational damage.
Phishing attacks continue to evolve, using a wide range of techniques to target individuals and organizations across North America. Whether through emails, phone calls, text messages, or fake websites, phishing remains one of the most effective and damaging forms of cybercrime. As the threat grows, businesses must remain vigilant and implement comprehensive cybersecurity measures to protect themselves from the potential consequences of these attacks.
Western I.T.’s WIT Learn training helps enable your team to see these phishing attacks coming and respond appropriately. Contact us today for more information!
1-800-752-4238
Understand the Holiday Season Cyber Threats The holiday season is a time for joy, celebration, and generosity....
Cybercriminals steal credit card? Cybercriminals have various methods at their disposal to hack and exploit credit...
This in-depth cybersecurity planning guide provides information and advice to help organizations develop a successful...