In today’s fast-paced business environment, effective communication is critical for success. Traditional phone systems, while...


In today’s fast-paced business environment, effective communication is critical for success. Traditional phone systems, while...
" Microsoft adds AI tools " New generative AI capabilities enhance real-time meeting notetaking by identifying each speaker and...

Generative AI has the potential to dramatically reshape how companies manage their VoIP communications. A more intelligent...

In today's dynamic business landscape, communication is the cornerstone of success. For Canadian small businesses, having a...
VOIP Phone London Ontario In the evolving landscape of Canadian business communication, VOIP phone technology is the gold...

Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP). Businesses are increasingly shifting from traditional Public-Switched Telephone Networks (PSTN) to modern Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) systems. This transition marks a significant change in how organizations communicate, offering a multitude of advantages over legacy phone systems. Unlike PSTN, which relies on circuit-switched networks to transmit voice, VoIP utilizes the internet to carry voice, video, and data, making communication more efficient and versatile.
VoIP is not just a technological upgrade; it’s a transformative innovation that reshapes business communication. This technology broadens the scope of traditional telephony, introducing benefits such as cost savings, enhanced flexibility, and a wealth of features that were previously unattainable. Key components of VoIP systems include robust network security measures, advanced data encryption, and seamless integration with existing business applications. By leveraging VoIP, businesses can achieve greater efficiency, scalability, and resilience in their communication infrastructure. This blog post delves into the comprehensive scope of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), exploring its critical components and the myriad benefits it offers to modern enterprises.
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) is a groundbreaking technology that allows voice communications and multimedia sessions to be transmitted over the Internet. Unlike traditional Public-Switched Telephone Networks (PSTN), which rely on circuit-switched networks for voice transmission, VoIP leverages packet-switched networks, making communication more flexible and cost-effective.
VoIP, or Voice over Internet Protocol, refers to a group of technologies and methodologies that enable the delivery of voice communications and multimedia sessions over Internet Protocol (IP) networks. Essentially, VoIP converts analog voice signals into digital data packets, which are then transmitted over the Internet or other IP-based networks. This approach differs significantly from the traditional PSTN, which establishes a dedicated circuit for the duration of a call, leading to inefficiencies and higher costs.
In the traditional PSTN system, a call is established by creating a continuous connection between the caller and the recipient. This circuit-switched network approach means that a dedicated pathway is maintained for the entire duration of the call, regardless of whether there is active communication taking place. This method, while reliable, is not efficient in terms of resource utilization, as it requires constant, dedicated bandwidth.
In contrast, Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) systems use packet-switched networks. In this method, voice data is broken down into smaller packets, each of which is transmitted independently over the network. These packets are reassembled at the destination, allowing for a more efficient use of network resources. Because packets can take the most efficient path to their destination, Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) can often provide higher quality and more reliable communications, even over long distances.
The basic working of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) involves several key processes, all designed to efficiently convert voice signals into digital data and back again, ensuring clear and reliable communication. Here’s a step-by-step overview of how VoIP works:
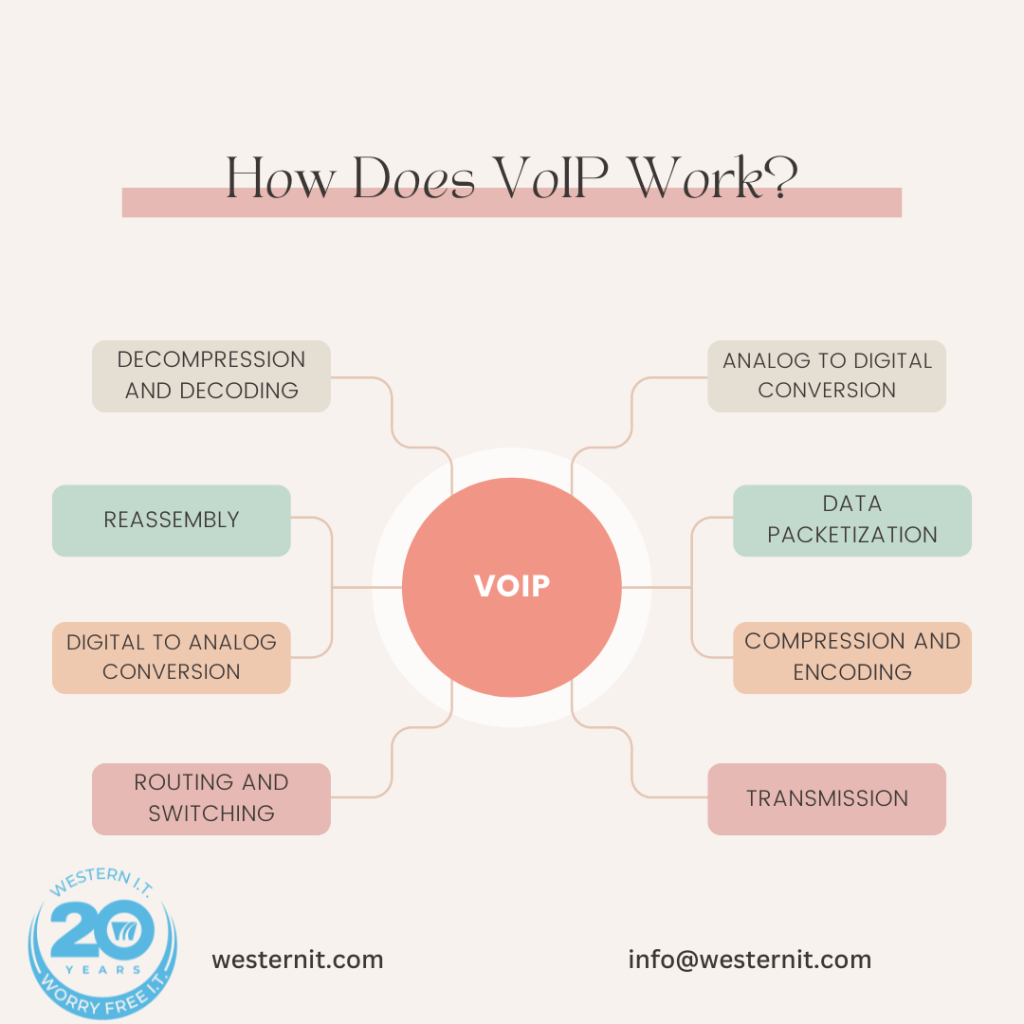
The advantages of using VoIP over traditional PSTN are numerous. Firstly, Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) significantly reduces the cost of communication by utilizing existing internet connections and avoiding the need for separate voice lines. This can result in substantial savings, particularly for businesses with high call volumes or international communication needs.
Additionally, VoIP systems offer greater flexibility and scalability. Businesses can easily add or remove lines and features as needed without significant infrastructure changes. VoIP also supports a wide range of advanced features, such as voicemail-to-email, call forwarding, video conferencing, and integration with other business applications, enhancing productivity and collaboration. Moreover, VoIP can improve communication quality and reliability. Modern VoIP codecs and Quality of Service (QoS) protocols ensure that voice data is transmitted with minimal latency and packet loss, providing clear and consistent audio quality even over long distances.
In summary, Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) is a transformative technology that leverages the efficiency and flexibility of the Internet to provide high-quality, cost-effective voice communications. By understanding its workings and advantages, businesses can make informed decisions about adopting VoIP to enhance their communication infrastructure.
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) systems rely on a robust infrastructure to deliver reliable and high-quality voice communications over the Internet. Understanding the key components of this infrastructure is essential for optimizing Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) performance and ensuring secure, efficient operation.
The Internet Protocol (IP) is the foundational technology that enables VoIP systems. IP is a set of rules governing the format of data sent over the internet or other networks. In Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), IP plays a crucial role by facilitating the transmission of voice data across networks in the form of packets.
IP operates at the network layer of the TCP/IP model, managing the addressing and routing of data packets from the source to the destination. Each device on the network is assigned a unique IP address, which is used to identify the sender and receiver of the data. IP ensures that packets are delivered to the correct address, even if they take different paths through the network. This flexibility is one of the reasons VoIP can efficiently utilize existing internet infrastructure for voice communication.
In VoIP systems, data packets are the fundamental units of communication. When you speak into a VoIP-enabled device, your voice is converted into digital data, which is then divided into small packets. Each packet contains a portion of the voice data and header information that includes the source and destination IP addresses and sequencing information.
The packetization process is critical for Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) because it allows voice data to be transmitted efficiently over the internet. Unlike traditional PSTN, which requires a continuous circuit for the duration of the call, VoIP packets can be sent independently and take the most efficient route to their destination. This method improves bandwidth utilization and reduces costs. Upon arrival, the packets are reassembled in the correct order to recreate the original voice message.
A gateway is a critical component in VoIP systems that facilitates communication between different networks, particularly between traditional PSTN and IP networks. Gateways perform several functions, including protocol conversion, data compression, and routing.
In a VoIP context, gateways convert analog voice signals from the PSTN into digital data packets that can be transmitted over IP networks and vice versa. This conversion allows for seamless communication between traditional phone systems and VoIP systems. Gateways also handle the compression of voice data to optimize bandwidth usage and may provide additional features such as call routing and signalling.
Firewalls are essential for securing VoIP systems against cyber threats and unauthorized access. A firewall is a network security device that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules.
In VoIP infrastructure, firewalls help protect voice data by preventing unauthorized access and mitigating various types of attacks, such as denial-of-service (DoS) attacks and eavesdropping. Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) traffic is typically allowed through the firewall on specific ports, ensuring that only legitimate traffic can pass through. Advanced firewalls, such as session border controllers (SBCs), provide additional security features tailored to VoIP, including encryption, intrusion detection, and quality of service (QoS) management.
A softswitch is a software-based switch that manages the routing of voice data in a VoIP network. Unlike traditional hardware switches, softswitches use software to perform call control and signalling functions. They are responsible for connecting calls between VoIP devices, managing user accounts, and handling various signalling protocols.
Softswitches play a central role in Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) networks by enabling efficient and flexible call management. They support various features such as call forwarding, conferencing, and voicemail. Softswitches can also integrate with other systems, such as customer relationship management (CRM) software, to enhance business communication capabilities.
Virtual Private Networks (VPN) and Wide Area Networks (WAN) are crucial for supporting VoIP systems, particularly in businesses with multiple locations or remote workers.
VPN: A VPN creates a secure, encrypted connection over a less secure network, such as the Internet. By using a VPN, businesses can ensure that VoIP traffic is protected from interception and unauthorized access. VPNs are particularly useful for remote workers, allowing them to securely connect to the corporate network and use VoIP services as if they were in the office.
WAN: A WAN connects multiple local area networks (LANs) over a large geographic area. For businesses with multiple locations, a WAN enables seamless VoIP communication across different sites. WANs ensure that voice data can be transmitted efficiently and securely, supporting features such as internal dialling and call transfer between locations.
The key components of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) infrastructure—Internet Protocol (IP), data packets, gateways, firewalls, softswitches, VPNs, and WANs—work together to provide a robust, flexible, and secure communication system. By understanding and optimizing these components, businesses can leverage VoIP technology to improve communication efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance overall productivity. VoIP systems offer significant advantages over traditional PSTN, making them an increasingly popular choice for modern business communication.
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) relies on a variety of technologies and standards to ensure efficient, reliable, and high-quality communication. Understanding these technologies is essential for businesses looking to implement or optimize their VoIP systems. Key technologies and standards in VoIP include Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), H.323, IP Private Branch Exchange (IP PBX), and Quality of Service (QoS).
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is a signalling protocol used to initiate, maintain, modify, and terminate real-time sessions that involve video, voice, messaging, and other communications applications and services. SIP is fundamental to the functionality of VoIP systems.
SIP works by defining the messages that are sent between endpoints and managing the actual establishment, management, and termination of communication sessions. These messages are sent in a text-based format, similar to HTTP, which makes them easy to understand and debug.
H.323 is an older but still relevant standard for real-time, packet-based multimedia communications. It was developed by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and is widely used in video conferencing, VoIP, and other IP-based communication services.
While SIP has largely overshadowed H.323 due to its simplicity and flexibility, H.323 remains in use, particularly in legacy systems and specific applications where its comprehensive feature set is beneficial.
An IP Private Branch Exchange (IP PBX) is a telephone switching system within an enterprise that switches calls between VoIP users on local lines while enabling all users to share a certain number of external phone lines. The main functions of an IP PBX include managing incoming and outgoing calls, voicemail, call routing, and other telephony services.
IP PBX systems can be either hardware-based or software-based. Hardware-based IP PBX systems use physical devices to manage calls, while software-based IP PBX systems run on standard computer servers, providing greater flexibility and scalability.
Quality of Service (QoS) refers to the performance level of a service, such as VoIP, and its ability to deliver data with high reliability and minimal delay. QoS is crucial for maintaining VoIP call quality, as voice and video communications are sensitive to delays, jitter, and packet loss.
Implementing QoS involves configuring network devices such as routers and switches to prioritize VoIP traffic. Techniques such as traffic shaping, priority queuing, and bandwidth reservation are used to ensure that VoIP calls receive the necessary resources to maintain high quality.
The technologies and standards behind VoIP—such as SIP, H.323, IP PBX, and QoS—are essential for enabling efficient, reliable, and high-quality communication. Understanding these components helps businesses leverage Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) technology to enhance their communication infrastructure, reduce costs, and improve overall productivity. VoIP represents a significant advancement over traditional telephony, providing a versatile and scalable solution for modern business communication needs.
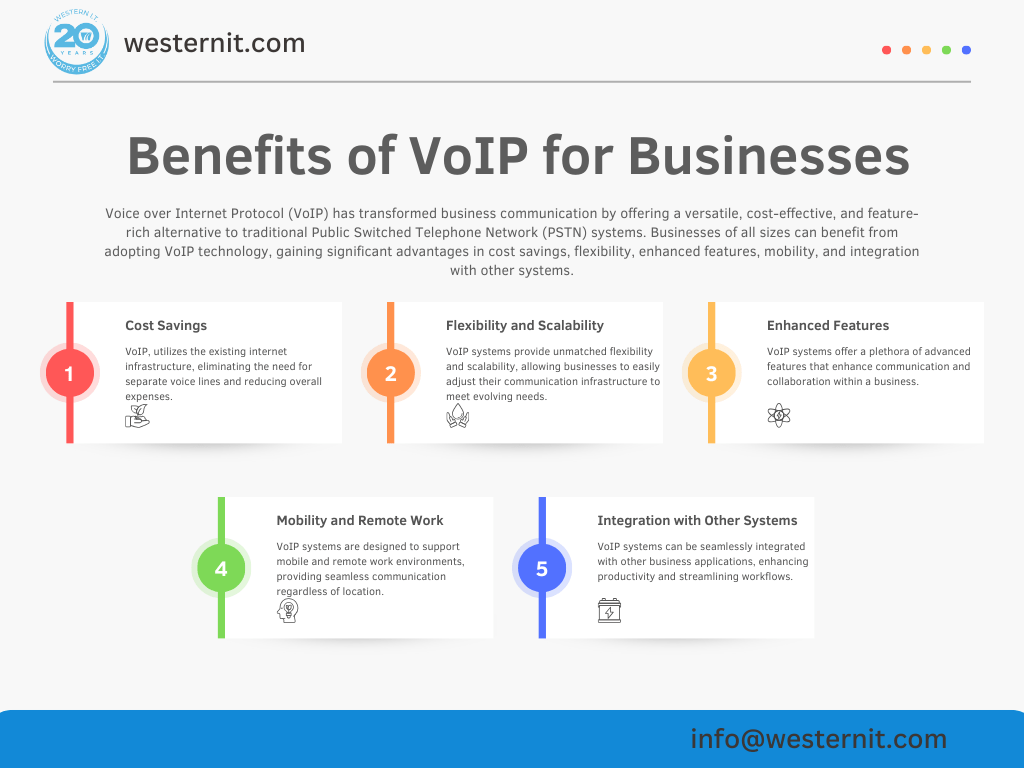
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) has transformed business communication by offering a versatile, cost-effective, and feature-rich alternative to traditional Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) systems. Businesses of all sizes can benefit from adopting VoIP technology, gaining significant advantages in terms of cost savings, flexibility, enhanced features, mobility, and integration with other systems.
One of the most compelling benefits of VoIP for businesses is the substantial reduction in communication costs compared to traditional PSTN systems. Traditional phone systems require dedicated phone lines for each call, leading to high setup, maintenance, and operational costs. VoIP, on the other hand, utilizes the existing internet infrastructure, eliminating the need for separate voice lines and reducing overall expenses.
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) systems provide unmatched flexibility and scalability, allowing businesses to easily adjust their communication infrastructure to meet evolving needs.
VoIP systems offer a plethora of advanced features that enhance communication and collaboration within a business. These features go beyond what traditional phone systems can offer, providing added value and improving overall efficiency.
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) systems are designed to support mobile and remote work environments, providing seamless communication regardless of location.
VoIP systems can be seamlessly integrated with other business applications, enhancing productivity and streamlining workflows.
VoIP offers a multitude of benefits for businesses, including cost savings, flexibility, enhanced features, support for mobility and remote work, and seamless integration with other systems. By adopting VoIP technology, businesses can improve communication efficiency, reduce expenses, and enhance overall productivity. VoIP is a powerful tool that enables modern businesses to stay connected, collaborate effectively, and adapt to changing needs in an increasingly digital world.
Adopting Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) in your business can significantly enhance your communication capabilities, improve efficiency, and reduce costs. However, transitioning to VoIP requires careful planning and consideration to ensure a smooth implementation. This section will guide you through assessing your business communication needs, selecting the right VoIP provider, understanding internet and bandwidth requirements, and exploring various VoIP hardware options.
Before transitioning to Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), it is essential to evaluate your business communication needs comprehensively. This assessment helps in determining the specific requirements and features that will best support your operations.
Selecting the right Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) provider is crucial for the success of your VoIP implementation. Here are some tips to help you make an informed decision:
Optimal VoIP performance depends on having a reliable internet connection and sufficient bandwidth. Understanding these requirements is essential to ensure high-quality voice communication.
Selecting the right hardware is an important aspect of implementing VoIP in your business. Here are some common VoIP hardware options to consider:
Transitioning to VoIP requires careful planning and consideration. By assessing your business communication needs, selecting the right VoIP provider, understanding internet and bandwidth requirements, and choosing the appropriate hardware, you can ensure a smooth and successful implementation. VoIP offers numerous benefits, including cost savings, flexibility, enhanced features, and support for remote work, making it a valuable addition to any modern business communication strategy.
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) has revolutionized business communication across various sectors. Its flexibility, cost-efficiency, and advanced features make it a valuable asset for organizations of all sizes. Here, we explore real-world examples and case studies of small businesses, large enterprises, and specific industries that have successfully implemented VoIP to enhance their operations.
Small businesses often face challenges related to limited budgets and resources. VoIP offers these businesses a cost-effective solution to improve communication and streamline operations.
Example 1: A Local Boutique A small boutique shop with a single location switched to VoIP to reduce its monthly phone bills and improve customer service. Before VoIP, the boutique struggled with high costs associated with traditional phone lines and lacked features like call forwarding and voicemail-to-email.
After implementing VoIP, the boutique experienced significant cost savings. The owner could manage calls more efficiently, forwarding them to mobile phones when staff were away from the shop. Voicemail-to-email ensured that no customer inquiries were missed, enhancing customer satisfaction. The boutique also utilized auto-attendant features to greet callers and direct them to the right department, creating a professional image.
Example 2: A Startup Tech Company A tech startup with a distributed team needed a reliable communication system that supported remote work and collaboration. VoIP provided the perfect solution with its flexibility and integration capabilities.
By adopting a VoIP system, the startup enabled its remote employees to stay connected through softphones and mobile apps. Features like video conferencing and instant messaging facilitated collaboration, while integration with project management tools streamlined workflows. The startup saved on infrastructure costs and enjoyed the scalability of VoIP, easily adding new lines as the team grew.
Large enterprises have complex communication needs that require robust and scalable solutions. VoIP helps these organizations improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance collaboration across multiple locations.
Example 1: A Global Manufacturing Company A global manufacturing company with offices and plants in multiple countries faced challenges with maintaining consistent and cost-effective communication. The traditional phone systems were expensive to maintain and lacked the flexibility to support the company’s growing needs.
The company transitioned to a VoIP system, connecting all its locations through a unified communication platform. This move resulted in substantial cost savings on international calls and reduced the complexity of managing multiple phone systems. Employees benefited from advanced features such as call forwarding, voicemail-to-email, and conference calling. The company also integrated VoIP with its CRM system, improving customer interactions and support.
Example 2: A Financial Services Firm A large financial services firm needed a secure and reliable communication solution to handle sensitive client information and regulatory requirements. VoIP provides the necessary security features and compliance capabilities.
The firm implemented a VoIP system with encryption and secure data transmission to protect client communications. Quality of Service (QoS) settings ensured that voice traffic was prioritized, maintaining high call quality. The firm also used VoIP’s conferencing features to hold virtual meetings with clients and remote employees, reducing travel costs and improving productivity.
VoIP’s versatility makes it suitable for various industries, each benefiting from tailored solutions that address specific communication needs.
Healthcare providers require reliable communication systems to ensure patient care and coordination among staff. VoIP offers features that enhance efficiency and improve patient experiences.
Example: A Regional Hospital A regional hospital implemented VoIP to replace its outdated phone system. The VoIP system integrated with the hospital’s electronic health records (EHR) system, allowing staff to access patient information during calls. Call routing and auto-attendant features ensured that patient inquiries were directed to the appropriate departments quickly. VoIP also supported telemedicine services, enabling remote consultations and reducing the need for in-person visits.
Retail Retail businesses benefit from VoIP’s ability to improve customer service and streamline operations across multiple locations.
Example: A National Retail Chain A national retail chain adopted VoIP to enhance communication between its headquarters and store locations. The VoIP system provided features such as call forwarding and unified messaging, ensuring that customer calls were handled promptly. The chain also used VoIP for internal communication, with features like group calling and instant messaging improving coordination among staff. The scalability of VoIP allowed the chain to easily add new locations to the system as it expanded.
Education Educational institutions use VoIP to facilitate communication between administrators, teachers, students, and parents.
Example: A University A university implemented VoIP to replace its traditional phone system, which was costly and difficult to manage. The VoIP system supported features like voicemail-to-email, call forwarding, and video conferencing, enhancing communication across the campus. Professors used VoIP for remote lectures and virtual office hours, while administrators benefited from the system’s integration with the university’s email and scheduling software. The university saved on operational costs and provided a modern communication solution that met the needs of its faculty and students.
VoIP has proven to be a versatile and valuable tool for businesses across various sectors. From small boutiques and tech startups to large manufacturing companies and financial services firms, VoIP offers significant benefits, including cost savings, flexibility, enhanced features, and support for remote work. Industry-specific applications in healthcare, retail, and education further demonstrate VoIP’s ability to meet unique communication needs and improve overall efficiency. By adopting VoIP, businesses can enhance their communication capabilities, streamline operations, and achieve greater success.
While Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) offers numerous advantages, it also presents several challenges that businesses must address to ensure successful implementation and operation. Understanding these challenges and implementing effective solutions is crucial for maximizing the benefits of VoIP technology.
Security is a significant concern when it comes to VoIP, as the transmission of voice data over the internet exposes it to various cyber threats. Common VoIP security issues include:
Solutions:
VoIP systems, while offering advanced features and cost savings, can also face technical challenges that need to be addressed to ensure smooth operation.
Bandwidth Management: VoIP requires sufficient bandwidth to function effectively. Inadequate bandwidth can lead to poor call quality, dropped calls, and service interruptions.
Network Configuration: Incorrect network configuration can cause issues such as jitter, latency, and packet loss, all of which can degrade VoIP call quality.
Compatibility Issues: Integrating VoIP with existing systems and hardware can sometimes lead to compatibility issues, causing service disruptions.
Solutions:
Maintaining high-quality VoIP calls is essential for ensuring effective communication and user satisfaction. Several factors can impact VoIP call quality, including network performance, hardware quality, and system configuration.
Latency: High latency can cause delays in voice transmission, leading to interruptions and poor call quality.
Jitter: Jitter refers to the variation in packet arrival times, which can cause choppy or distorted audio.
Packet Loss: Loss of data packets during transmission can result in missing audio segments and degraded call quality.
Solutions:
While VoIP offers numerous benefits for businesses, addressing the associated challenges is crucial for successful implementation and operation. By implementing robust security measures, addressing technical difficulties, and ensuring high call quality, businesses can fully leverage the advantages of VoIP technology. Understanding these challenges and solutions helps in creating a resilient and efficient communication system that supports business growth and productivity.
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) has undergone significant transformations since its inception, continuously adapting to technological advancements and changing communication needs. As we look to the future, several key trends are set to further enhance VoIP capabilities and integration. These trends include the incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI), the integration with Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and the impact of 5G technology on VoIP performance and adoption.
Artificial intelligence is poised to revolutionize VoIP by introducing advanced features and capabilities that enhance user experience, efficiency, and security.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a rapidly growing network of interconnected devices that communicate and share data. Integrating Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) with IoT devices opens up new possibilities for seamless and efficient communication.
The rollout of 5G technology promises to significantly impact VoIP performance and adoption. 5G networks offer higher speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity compared to previous generations of mobile networks, which are crucial for enhancing VoIP capabilities.
The future of VoIP is shaped by exciting advancements in AI, IoT integration, and the deployment of 5G technology. These trends will enhance VoIP capabilities, making communication more efficient, flexible, and secure. By staying abreast of these developments, businesses can leverage VoIP to improve their communication infrastructure, support remote work, and drive growth in an increasingly connected world. As VoIP continues to evolve, it will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of business communication.
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) has revolutionized modern business communication, providing numerous benefits that enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and support the evolving needs of businesses in an increasingly digital world. As we’ve explored throughout this discussion, VoIP offers a robust, flexible, and scalable solution that outperforms traditional Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) systems in several critical areas.
Given the substantial benefits and transformative potential of VoIP, it is clear that businesses looking to stay competitive and agile in today’s fast-paced environment should seriously consider adopting VoIP solutions. The move to VoIP not only addresses current communication challenges but also positions businesses for future technological advancements.
For businesses considering this transition, partnering with a reliable and experienced provider is crucial. Western IT is a leading provider of comprehensive Voice over Internet Protocol VoIP and managed IT services, offering tailored solutions designed to meet the unique needs of each business. With a deep understanding of VoIP technology and a commitment to customer satisfaction, Western IT ensures that your communication infrastructure is robust, secure, and future-ready.
Why Choose Western IT for Your VoIP Needs?
To explore how Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) can transform your business communication and to learn more about our comprehensive VoIP and managed IT services, contact Western IT today. Our team is ready to assist you in assessing your needs, designing a customized VoIP solution, and providing ongoing support to ensure your business thrives in the digital age. Embrace the future of communication with Western IT and experience the benefits of a modern, efficient, and scalable VoIP system.
The Rise of VoIP in Michigan: A Game Changer for Remote Work Over the past decade, VoIP in Michigan has evolved from a...
In today’s fast-paced business environment, effective communication is critical for success. Traditional phone...
" Microsoft adds AI tools " New generative AI capabilities enhance real-time meeting notetaking by identifying each...